What is photovoltaic power station? Introduction to the application of solar panels
A photovoltaic (PV) power station, also known as a solar power plant or solar farm, is a large-scale installation designed to convert sunlight directly into electricity using photovoltaic technology. Here‘s an overview of photovoltaic power stations and the application of solar panels:
Photovoltaic Power Station
Definition and Working Principle
Definition: A photovoltaic power station is a large-scale solar energy system that uses photovoltaic panels to capture sunlight and convert it into electrical power. These systems are typically connected to the electrical grid to supply electricity to the grid or to specific locations.
Working Principle: Photovoltaic cells, typically made from semiconductor materials like silicon, generate electricity when exposed to sunlight. This process is known as the photovoltaic effect. When sunlight hits the PV cells, it excites electrons, creating an electric current.
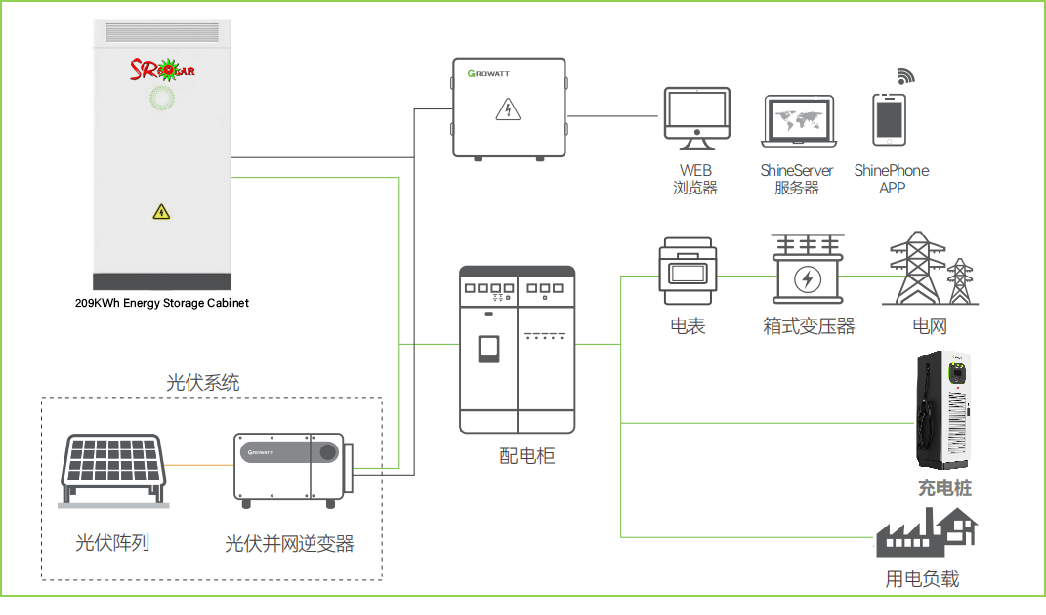
Key Components
Solar Panels (PV Modules): The primary component that captures sunlight and converts it into direct current (DC) electricity.
Inverters: Convert the DC electricity generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity, which is used by most electrical devices and can be fed into the electrical grid.
Mounting Systems: Structures that support and orient the solar panels to maximize sunlight exposure. They can be fixed or equipped with tracking systems to follow the sun‘s path.
Balance of System (BOS): Includes wiring, switches, fuses, and other electrical components necessary to connect and manage the power system.
Transformers and Substations: Step up the voltage of the generated electricity to match the grid requirements.
Applications of Solar Panels
Residential Use
Rooftop Solar Systems: Solar panels are installed on the rooftops of homes to generate electricity for personal use, often with excess power fed back into the grid.
Off-Grid Systems: Used in remote areas without access to the grid, often paired with battery storage to provide continuous power.

Commercial and Industrial Use
Commercial Buildings: Large installations on rooftops or as part of building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) to reduce electricity costs and reliance on the grid.
Industrial Applications: Solar panels used in factories and large facilities to lower operational costs and carbon footprint.
Utility-Scale Solar Farms
Large-Scale Generation: Solar farms cover large areas with thousands or millions of solar panels to generate significant amounts of electricity, feeding it directly into the grid.
Community Solar Projects: Shared solar installations where multiple users can subscribe to receive a portion of the generated electricity.
Specialized Applications
Agrivoltaics: Combining agriculture and solar power generation by installing solar panels over crops, providing shade and reducing water usage.
Floating Solar Farms: Solar panels installed on bodies of water, such as reservoirs or lakes, which helps in reducing land usage and cooling the panels, improving efficiency.
Solar-Powered Infrastructure: Used in powering streetlights, traffic signals, and other infrastructure components in cities and rural areas.

Advantages of Photovoltaic Power Stations
Clean Energy: Solar power generation produces no greenhouse gases or pollutants, contributing to a reduction in carbon footprint.
Renewable Resource: Sunlight is an abundant and inexhaustible resource, making solar power a sustainable option.
Low Operating Costs: After the initial installation, solar power plants have low maintenance and operating costs.
Energy Independence: Reduces dependence on fossil fuels and enhances energy security.



